speech to text e2e usecase API
overview
I’ve set up a clean architecture for the ai repository and containerized it. this pipeline is deployed on a remote server ready for action.
background
requirements
we need to develop a speech API that allows users to communicate with golem NPCs. in a Unity-based game, users activate their microphones locally, send the recorded audio to the server, and receive NPC responses in text form.
priorities
- first, complete the speech transcript to text-to-text pipeline.
- ensure smooth API communication on the remote server.
- focus on reducing latency as much as possible.
secondary priorities
- prompt tuning
- enhance security with the WSS protocol
purpose
to build a speech-to-text and text-to-text API that operates reliably on a remote server.
environment setup
- managing dependencies with uv and pyproject.toml
- server IP address: http://44.210.134.73:8000/docs
- api endpoint: ws://44.210.134.73:8000/api/v1/ws/speech/v1
- we handle dependencies with clean architecture through container implementation and injection.
implementation process
design
- architecture: DDD + clean architecture
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
demo/src/ai
├── datasets # testfile
├── docker-compose.yaml
├── Dockerfile
├── interaction
│ ├── core
│ │ ├── components #llm and speech component
│ │ ├── di
│ │ │ ├── config.py
│ │ │ └── container.py
│ │ ├── domain
│ │ │ └── usecase
│ │ ├── infra
│ │ │ ├── model_configs.py
│ │ │ └── model_router.py #litellm Router
│ │ └── utils
│ ├── server
│ │ ├── app.py
│ │ ├── core
│ │ │ └── session_manager.py #for ws session managing
│ │ ├── dto
│ │ │ └── speech.py
│ │ ├── router
│ │ │ └── speech
│ │ │ └── v1.py
│ │ └── tests # test server files
│ │ └── test_websocket_speech.py
│ ├── speech
│ │ ├── components
│ │ │ ├── speech_to_text
│ │ │ │ └── llm_speech_to_text_v1.py
│ │ │ └── text_to_text
│ │ │ └── llm_text_to_text_v1.py
│ │ ├── di
│ │ │ └── container.py
│ │ ├── domain
│ │ │ ├── ports
│ │ │ │ ├── speech_to_text.py
│ │ │ │ └── text_to_text.py
│ │ │ └── usecases
│ │ │ └── generate_conversation_response.py
│ │ ├── main.py
│ │ ├── prompts
│ │ │ └── text_to_text_v1.py
│ │ └── tests
│ │ ├── test_speech_to_text.py
│ │ └── test.py
│ └── text
├── Makefile
├── pyproject.toml
└── uv.lock
implementing the domain-driven design approach with a focus on clean architecture principles ensures robust application structure and maintainability.
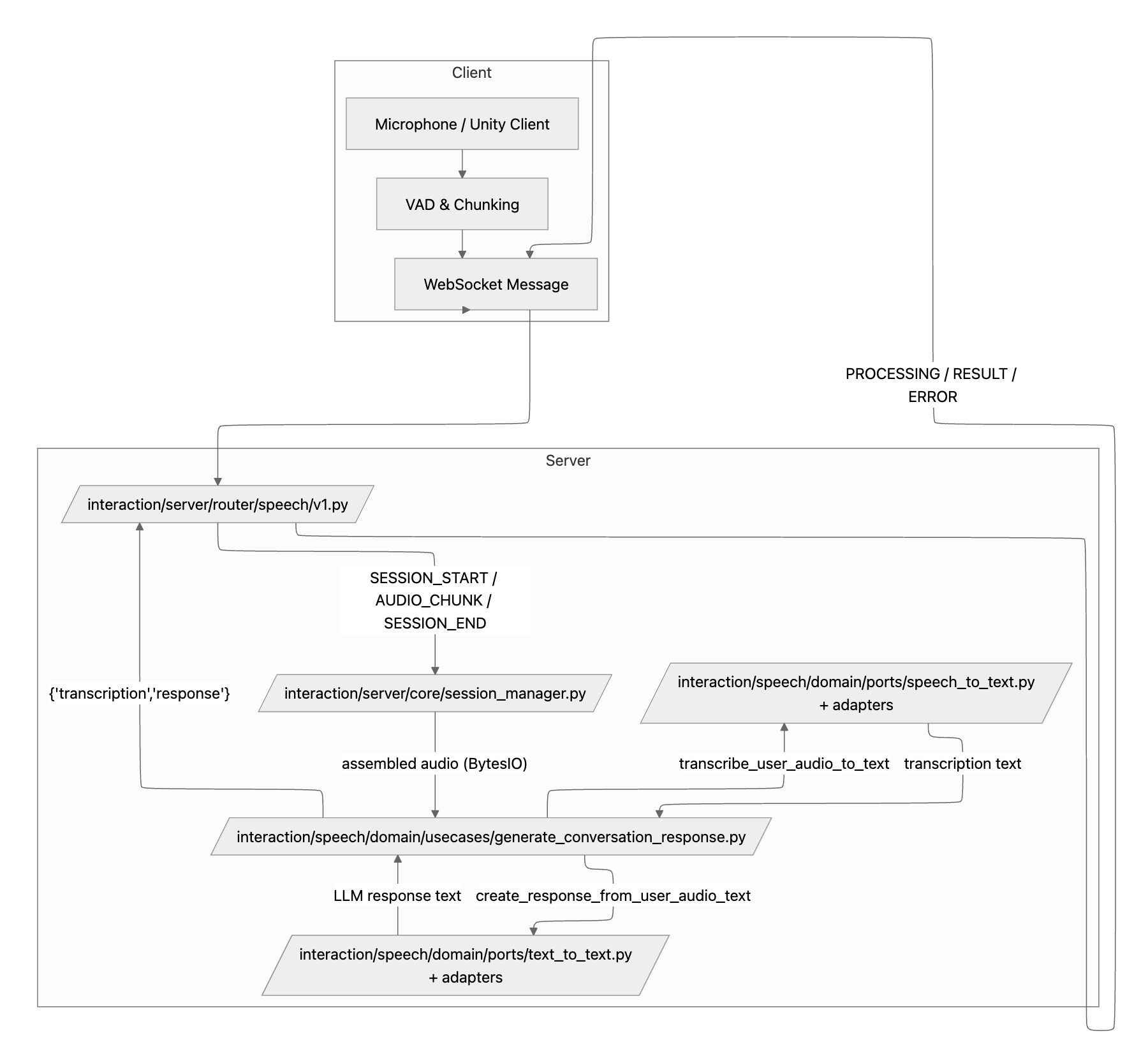
diagram is as follows:
flowchart LR
subgraph Client
Mic[Microphone / Unity Client]
VAD[VAD & Chunking]
WS[WebSocket Message]
end
subgraph Server
Router[/interaction/server/router/speech/v1.py/]
SessionMgr[/interaction/server/core/session_manager.py/]
UseCase[/interaction/speech/domain/usecases/generate_conversation_response.py/]
STT[/interaction/speech/domain/ports/speech_to_text.py<br/>+ adapters/]
TTT[/interaction/speech/domain/ports/text_to_text.py<br/>+ adapters/]
end
Mic --> VAD
VAD --> WS
WS --> Router
Router -->|SESSION_START / AUDIO_CHUNK / SESSION_END| SessionMgr
SessionMgr -->|"assembled audio (BytesIO)"| UseCase
UseCase -->|transcribe_user_audio_to_text| STT
STT -->|transcription text| UseCase
UseCase -->|create_response_from_user_audio_text| TTT
TTT -->|LLM response text| UseCase
UseCase -->|"{'transcription','response'}"| Router
Router -->|PROCESSING / RESULT / ERROR| WS
WS --> Client
result
- splitting an audio file
/datasets/test.wavinto chunks and requesting through the API gives expected results. logging indicates successful test completion.
pr
https://github.com/ob1hnk/Triolingo/pull/1
troubleshooting
- encountered issues with connecting the speech component to the router through litellm, which was resolved by aligning the implementation with existing components for consistency.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class SpeechLLMComponent:
"""
speech-to-text component using Router
"""
def __init__(self, router: Router, prompt_path: str = ""):
"""
Args:
router: LiteLLM Router instance
prompt_path: path to prompt file
"""
self.prompt_path = prompt_path
self.router = router
logger.info(f"SpeechLLMComponent initialized with prompt_path: {prompt_path}")
checked the litellm code thoroughly and resolved integration issues.
ref docs